Though world is covered with two thirds of water from the sea, unfortunately the quality of water is below par either for human consumption or irrigation and for many industrial applications.
Desalination refers to any process that removes excess salt and other minerals from water to obtain fresh water suitable for potable and other uses.
Three principle methods of desalination are namely thermal, electrical, and pressure. The oldest method, thermal distillation, has been around for thousands of years. In thermal distillation, the water is boiled and then the steam is collected, leaving the salt behind.
The second method is by using a thermal gradient evaporation and the third one uses the principle of using a pressurized semipermeable membrane between water of higher and lower salinity by reverse engineering the normal process of concentration gradient techniques, ie water flows from a higher concentration to a lower concentration, called Reverse Osmosis. Reverse Osmosis desalination technology does not need natural freshwater resources, desalination equipment can produce fresh water from seawater.
For community water supply the cheapest source is from rainwater or from other running river water streams provided they are not contaminated. With rapid urbanization and indifferent monsoon, the pressure for quality water exponentially increases both for human consumption and for industrial use. Scant respect for management of water conservancy and its dwindling resources adds additional stress on water requirement. The vey reason Niti Ayog flagged an alarm to the Jal Sakthi Ministry about probable zero dates of absolute droughts in various States in India. NITI Aayog is reportedly planning to set up desalination plants to leverage India’s vast coastline. The proposal talks about setting up plants along the 7,800-km coastline to make sea water potable, which could then be supplied around minor cities through a network of pipes.
The floating desalination plant in sea will leverage solar energy or ocean energy to reduce their carbon footprint and energy cost. Low temperature thermal desalination from sea water is also being constructed in Lakshadweep with a flash evaporator and condenser. However, these technologies are suitable for small towns in rural area and if the plants are interconnected the energy cost for pumping long distances would be highly cost prohibitive and commercially unviable. Some experts are of the view that desalination will have a limited role in solving India’s water woes because it will only address the water problem in coastal cities.
Desalination plant s operate in more than 120 countries in the world, including Saudi Arabia, Oman, United Arab Emirates, Spain, Cyprus, Malta, Gibraltar, Cape Verde, Portugal, Greece, Italy, India, China, Japan, and Australia. Many water starved countries (Israel, Gulf, African some EU and US) needing water for human and other consumption have resorted to Reverse Osmosis. This is more so considering the increasing population combined with the existing availability of scanty water resources. The two main types of desalination technologies – are namely membrane (RO) and thermal (MED, MVC and MSF).Reverse Osmosis (RO) desalination uses the principle of osmosis to remove salt and other impurities, by transferring water through a series of semi-permeable membranes to provide around 100 lpcd (litre percapita daily) of clean water. The largest water desalination plant is the Jubail Plant (Saudi Arabia) which produces 1,401,000 m³ (308,176,916.9 UK gal 370,105,045.4 US gal) daily, in Saudi Arabia, as verified on 14 January 2019 corresponding to a capacity of 1401 MLD. The largest desalination plant in the United States generates roughly 8 percent of San Diego County’s water supply.
As per latest trends to meet the water demand it has been pegged at about 25-30% of its requirements from desalination on an average, although some of the Gulf countries like Saudi Arabia touches as high as about 50%.The good blend however should be around 25-30% of the countries water requirement from desalination by environmentally friendly countries, even the very small country like Singapore, which has the best water management practice in Asia.
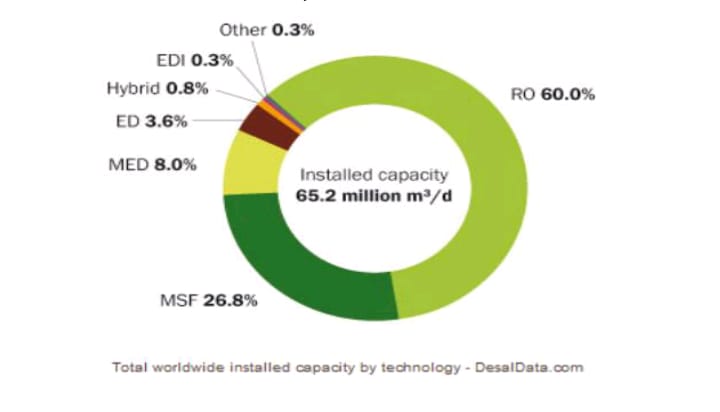
The spread of various desalination technology and processes used are depicted as under. This was the case about 5 years back.
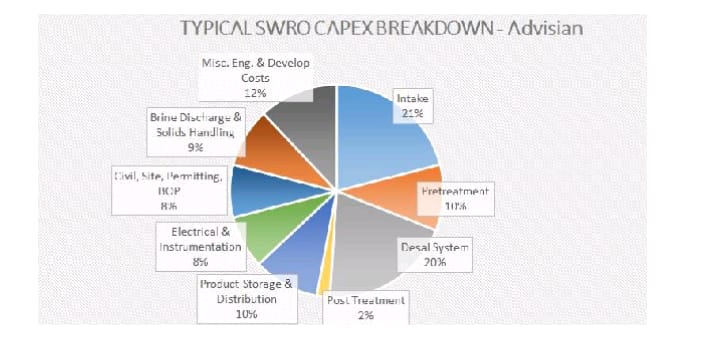
The rough capex cost matrix of a sea water RO plant of a relatively large size meant for large city community close to the coast is as under:
The approximate opex requirement of the same plant is depicted as under:
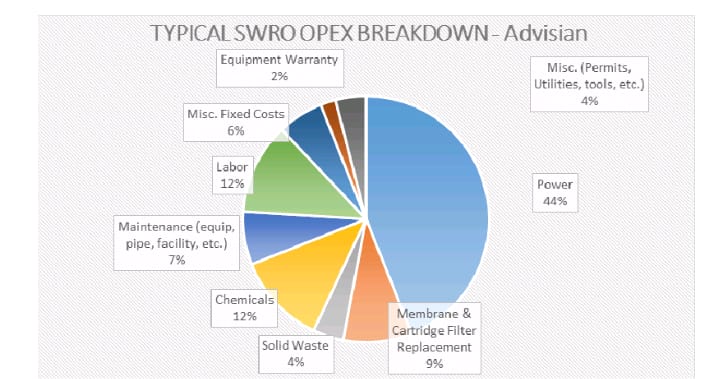
About 50% of the Capex (Capital Expenses) is attributable to three main components intake, RO plant and brine disposal, and the about 44% of the opex (Plant operational expenses)
A typical flow chart of a RO plant is depicted as under:

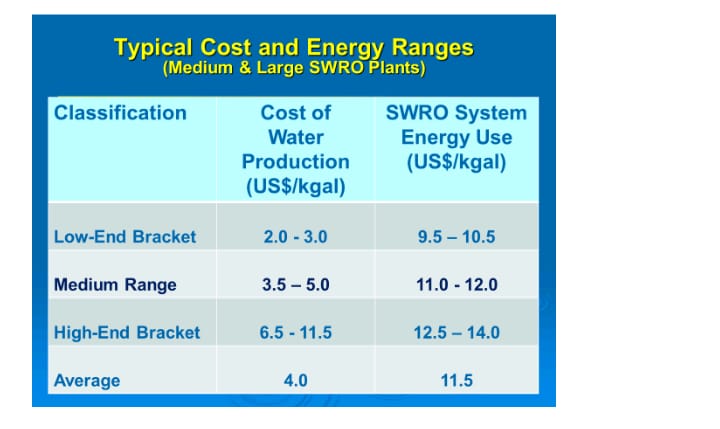
Cost of energy requirements for production of desalinated water for various brackets also shows a considerable variation as under:
Key Reasons for Cost Disparity Between High-End & Low-end Cost Projects
Desalination Site Location (closeness to sea proximity)
Costly Plants Have Overly Long Product Water Delivery Pipelines (Transmission Points of final delivery of water)
Environmental Considerations (Ecology oriented) **
Complex Intakes & Diffuser Systems (Ocean Engineering parameter oriented)**
Phasing Strategy (Building up common facility for intake and outfall for the ultimate capacity is necessary & would be idle investments if scale up RO membrane trains are built in stages)
Intake and Discharge System Capacity—Complexity of design based on environmental statutes
Pretreatment & RO System Design (dependent on sea water quality available at plant premises and subject to weather conditions)
Labor Market Pressures (Country and people specific)
Method of Project Delivery – Bidding process with clear cut defined terms of reference ie EPC (Engineering Procurement & Construction Mode), DFBOT (Design, Finance, Build, Operate and transfer to project authorities based on water purchase agreement and concession period to municipal authorities.
Risk Allocation—The project during the conceptualization stage should clearly study the environmental impact that could be created during construction and during operation to the marine ecology, address the livelihood of fishermen who do local near shore fishing activity, The reject water post reverse osmosis will be very much higher to the salinity of normal sea conditions with a very slight increase in temperature and is therefore to be discharged deeper ie below the 8- 9 m sea bed contour by subsea buried pipelines. MoEf has clear guidelines in India which insists on a REIA (Rapid Environmental Impact Assessment) with clear cur EMP (Environmental Management Plan) to be observed routinely, recorded and to be inspected by PCB (Pollution Control Boars).
Risk Opportunities— Technology developed in the last decade have aimed at developing by products which could be generated during high saline reject water back to the sea by exploring options of producing various salts, improving the recovery ratio of permeate water (the treated RO water), production of sodium hydroxide (Caustic Soda) plants (Currently under R&D) & energy recovery systems.
About Author

R.S.Kumar, Managing Partner Varaha Pipeline Engineering & Business Solutions LLP & Marine Specialist Project Consultant (RO) for community plants developed by Government Projects in Tamilnadu, Andra Pradesh, Maharashtra & Gujarat.
Kumar is”chemical engineer with about 40 years of experience.


























 WhatsApp us
WhatsApp us
Pingback: https://www.kirklandreporter.com/reviews/phenq-reviews-fake-or-legit-what-do-customers-say-important-warning-before-buy/
Pingback: เน็ต ais รายวัน