(Acknowledgement: The details and data are provided by Dr. S Nema, Scientist at Institute of Plasma Research, Ahmadabad.)
THE EXPANSIVE WASTE:
Disposal of solid wastes generated at various sources is one of the biggest problems faced by every country and especially in urban India. With growing population and growing demand more solid waste are generated. Over the years Plastic has replaced many utility items in our day to day life. Every Country & city waste management spends substantial amount on collection and transportation and maintaining dumping sites. The dumping sites by themselves create so many challenges and health risks for the people engaged in handling waste.
While other organic wastes get disposed easily with time, plastic causes maximum environmental risks. Various state governments have come up with stricter policies of banning polythene bags and plastic items as the half-life of plastic and polythene bags is very long and practically un-destroyable. Burning of plastics and polythene bags also causes dangerous toxic gases.
Institute of Plasma Research, Bhat, Gandhinagar, Gujarat is engaged in research of USAGE OF PLASMA for handling wastes from various Industries like textiles, hospitals, hotels, and Organic Waste.
Technical details of Plasma Pyrolysis System
Plasma pyrolysis is the process of thermal disintegration of organic mass into lower hydrocarbon in oxygen starved condition. Plasma Pyrolysis system (shown in Figure) comprises of various subsystems such as Plasma torch, Primary chamber, Secondary chamber, Venturi, Secondary scrubber, Demister and Electrostatic precipitator.
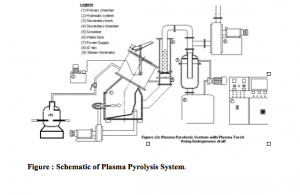
Plasma torches are ANODE & CATHODE Polarity generated by HIGH VOLTAGE. When any organic substance is kept between these polarities in absence of oxygen, it burns to plasma state producing hot gasses but leaves no waste. The hot gases thus generated are used in steam generation which in turn can be used for power generation. Also, the plastic and polythene butnt under plasma conditions do not generate the toxic gasses and leave no waste behind. The pilot unit was tested by Pollution Board and found that the emissions generated were within the limits and approved the process.
THE UNIT UNDER TEST BY POLLUTION BOARD AUTHORITIES

Table1: Emission Measurements in Plasma Pyrolysis System
Pollutants CPCB standards Emissions from Plasma
|
POLLUTANTS |
CPCB STANDARS |
EMISSION FROM PLASMA PROCESS |
|
CO |
< 100mg / Nm3 |
40 – 85 mg / Nm3 |
|
NOx |
< 400mg / Nm3 |
7 – 25 mg / Nm3 |
|
PM |
< 50mg / Nm3 |
31 – 52mg / Nm3 |
|
Dioxins & Furans |
<0.1ng / Nm3 TEQ |
0.01 – 0.1ng / Nm3 TEQ |
50kg/hr Plasma Pyrolysis System
FCIPT had developed and successfully demonstrated higher capacity system of 50 kg/hr which was funded by DST (illustrated in Figure). Several experiments were carried out for 2 months using heater (~ 20 kW) and DC power source (~ 35kW) in the primary chamber. The system was operated 4-6 hours every day. In this system, simulated biomedical waste (60%cotton +30%plastic +10%moisture) was disposed and exhaust gases were analysed for NOx, CO, dioxins and furans. It was observed that all emissions were well under the norms prescribed by CPCB.

GIFT CITY, a smart city started in Gandhinagar by Narendra Modi when he was CM of Gujarat.

Advanced version of Plasma Pyrolysis System
Recently in March 2017, in consultation with FCIPT, the technology licensing partner M/s B L Engineering successfully installed and commissioned a pilot plant of 150 kg/day capacity for safe disposal of paper, plastic and STP waste. This is fully automatic system in which the waste is fed from nearly 30 meters from the plant. There are many sensors for temperature measurement, water flow, waste availability, ID fan functioning, motor operation check etc. The whole plant is run by PLC and HMI based control operation. The system disposed 1500 kg of waste during trial runs at GIFT City.

CPCB Analysis Report
There were 32 analysis conducted by FCIPT with support from DST at various locations in India. The emission results are mentioned in table 1. A report was submitted to DST on this analysis which clearly indicates that the emissions of the gases were well below the norms given by CPCB.
(ii)Emission Measurements with Plastic Waste Disposal:
In a separate project activity with CPCB for safe disposal of plastic waste which include polyethylene bags, soiled plastic, metallized plastic, multi-layer plastic and PVC plastic using plasma pyrolysis technology, FCIPT carried out emission measurements while disposing these various categories of plastic waste. All the emissions were found below the norms given by CPCB, US-EPA.
CONCLUSION:
Plasma Technology is suitable to handle the menace of Plastic Waste and Medical waste generated at various sources and the hot air generated can be utilised for power generation that will minimise the expenses incurred on collection and transportation when these units are installed as part of commercial and domestic projects.
The Author, Jagdish Sethi, is a Mechanical Engineer from IIT-Rourkee and a Project Management Consultant.
The author can be followed in twitter at @jcsethi




























 WhatsApp us
WhatsApp us