Electricity generation is among the major causes of climate change around the globe. Most of our electricity comes from nonrenewable energy sources like coal, nuclear, and other sources. Producing energy from these resources has a severe impact on our environment, polluting our air, land, and water.
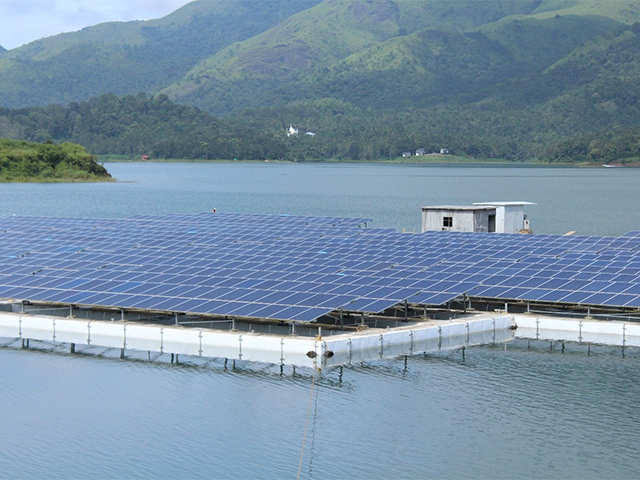
Clean energy development is an important key against climate change and limiting its most devastating effects. On similar lines, our nation is en route to India’s biggest floating solar plant to date. The plant is in the final developing stages and is likely to be commissioned by May this year.
India’s biggest floating solar plant
India’s biggest floating solar plant till date is being developed in Telangana’s Ramagundam and is likely to be commissioned by May this year.
It is one of the solar plants being developed by NTPC (National Thermal Power Corporation Limited), which is all set to commission around 217 MW (Megawatt) floating solar capacity in the coming days. Besides the 100 MW plant at Ramagundam, the other renewable energy plants that are lined up this year are 92 MW floating unit at Kayamkulam gas plant in Kerala and 25 MW unit at Simhadri power plant.
The concept of floating solar plant will enhance our Clean energy developments across the nation. These renewable powerplants will contribute to fulfilling the countries need for energy in an eco-friendly and effective manner.
Floating Solar: What you need to know
Generally, solar panels are installed on the ground or roof in small projects, but a large project usually covers large landmasses. But a newer alternative has been used quite frequently in the solar industry, which is floating solar.
What is floating solar? How do floating solar panels work?
Floating solar – also known as floating photovoltaic (FPV) or floatovoltaics. The solar array floats on top of a waterbody or a reservoir. Solar panels need to be affixed to a buoyant structure as that allows the solar panels to be above the ground.
Usually, the floating solar installations are likely to be located in a lake or basin because the waters are generally calmer than the ocean. It’s also common to install floating solar structures on large, man-made bodies of water, such as reservoirs.
Advantages of Floating solars
Valuable land space is conserved
The biggest advantage of floating solar panels is that the installations do not require valuable land space. The floating solars can be set up on unused space on water bodies, Many of these installations can take up unused space on bodies of water, such as hydroelectric dam reservoirs, wastewater treatment ponds, or drinking water reservoirs.
Higher solar panel performance
Solar panels are made to withstand high temperatures. But other electronics in the plant can be damaged under high temperature which can affect the plant output. Solar panel performance tends to decline as temperatures rise but the water bodies that host floating solar arrays help cool down the solar equipment, which means the panels produce electricity at higher efficiencies in hot climates than they might otherwise.
Environmental benefits
The floating solar panel structure shades the body of water and reduces evaporation from these ponds, reservoirs, and lakes. This is a particularly useful benefit in areas susceptible to drought, as water loss to evaporation can add up over time and contribute to a shortage.
The shade provided by the floating solar arrays helps to reduce the formation of algae in freshwater bodies.



























 WhatsApp us
WhatsApp us