In order to achieve the goal of self-reliance in India’s satellite-based navigation and augmentation services sector, a comprehensive and substantive policy for satellite-based navigation has been proposed. The draft of the Indian Satellite Navigation Policy – 2021 (SATNAV Policy – 2021) has been presented on the official website of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) that seeks public consultation, after which, the draft would be placed before the Union Cabinet for approval and authorization.
The draft states that it tends to “Achieve self-reliance in satellite-based navigation and augmentation services with an emphasis on assuring availability & quality, enhancing usage, working towards progressive evolution of the services and promoting research & development.”
Space-Based Navigation Systems
With the advent of rapid development of communication & information and mobile phone technology, crores of users across the nation are dependent on PVT (Position, Velocity, and Time) based applications for almost every task that happens virtually in their lives. Over the last few decades, there has been tremendous growth in the number of applications that depend on Position, Velocity, and Time (PVT) services that are provided by space-based navigation systems.
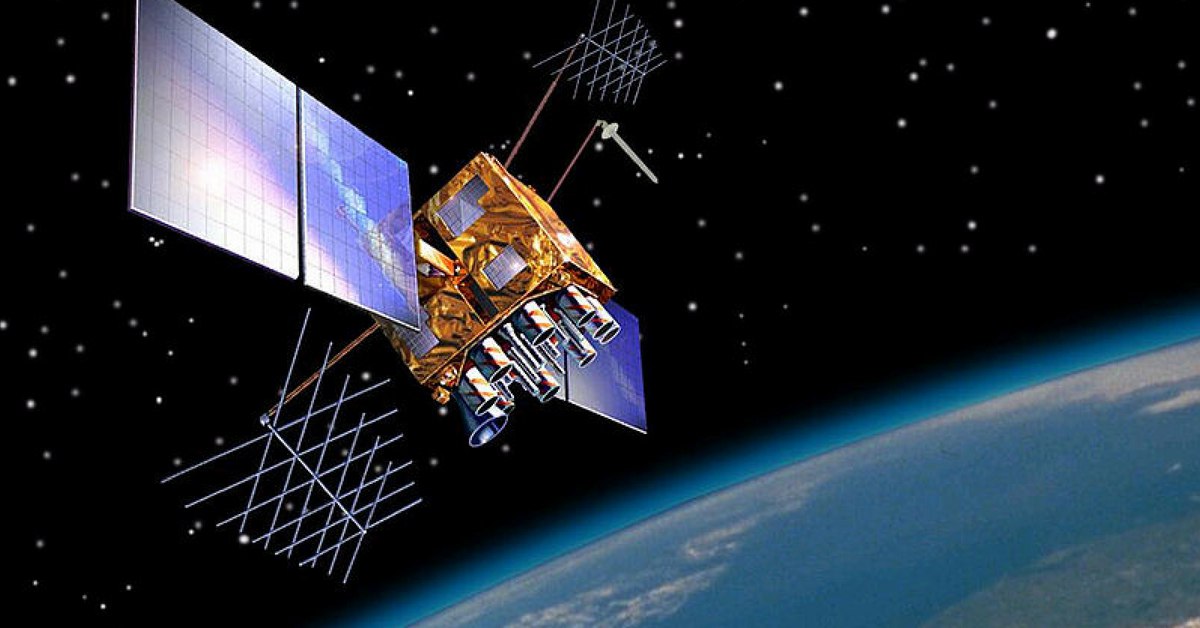
Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) is a general term describing a space-based navigation system that provides positioning, navigation, and precise-time (PNT) services on a global or regional basis. Currently, there are four GNSS:
– GPS: The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a satellite-based radio navigation system owned by the USA and operated by the United States Force.
– GLONASS: A Russian space-based satellite navigation system is a GNSS that provides an alternative to GPS and is the second navigational system with global coverage, freely available to all.
– Galileo: A global GNSS was created in 2016 by European Space Agency.
– BeiDou: The BeiDou Navigation Satellite System is owned and operated by the People’s Republic of China. It consists of two separate satellite constellations.
In addition to this, there are two regional navigation satellite systems
NavIC: With the operational name NavIC, the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System is an independent regional navigation satellite system developed by India. It provides accurate, precise, and real-time positioning and services. The satellite covers India and a region extending 1,500 km around.
QZSS: The Quasi-Zenith Satellite System, also known as Michibiki, is a regional GNSS owned by Japan and operated by QZS System Service. It is a four-satellite regional time transfer system, enhancing the United States-operated Global Positioning System in the Asia-Oceania regions, with a focus on Japan.
Indian Satellite Navigation Policy – 2021
The policy has been formulated with the objective to address the growing demands of space-based navigation and timing applications, with the view of self-sustenance in areas of commercial, strategic, and societal applications to maximize the socio-economic benefits. For a variety of applications, navigation signals are offered free-to-air. These applications include tracking, telematics, location-based services, automotive, survey, mapping & GIS, and timing.
According to the draft, there is a need for such secured services that are exclusive to the Indian strategic community.
The objective of the draft is to ensure the continuous availability of free-to-air navigation signals for civilian uses and secured navigation signals for strategic uses in the defined coverage area. For aviation safety in the defined coverage area, the draft ensures guaranteed and continuous availability of the Satellite-Based Augmentation System (SBAS). The draft also aims to focus on technology development for enhancing the navigation satellite systems and work towards compatibility and interoperability of Indian satellite navigation and augmentation signals with other GNSS/SBAS signals.
Further to intensify the Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative, the draft ensures continuity of NavIC and GAGAN services, upgrading the system and ensuring the capability to operate in conjecture with other GNSS/SBAS. Hence, according to the Department of Space, it is pertinent to devise a substantive national policy to boost national infrastructure.





















 WhatsApp us
WhatsApp us